In the realm of maritime logistics, Rail-Mounted Gantry (RMG) container cranes stand as stalwarts of efficiency, facilitating the seamless movement of containers within ports and terminals. This article aims to unravel the intricate working principle behind RMG container cranes, shedding light on the technology that enables these giants to lift and transport heavy containers with precision.
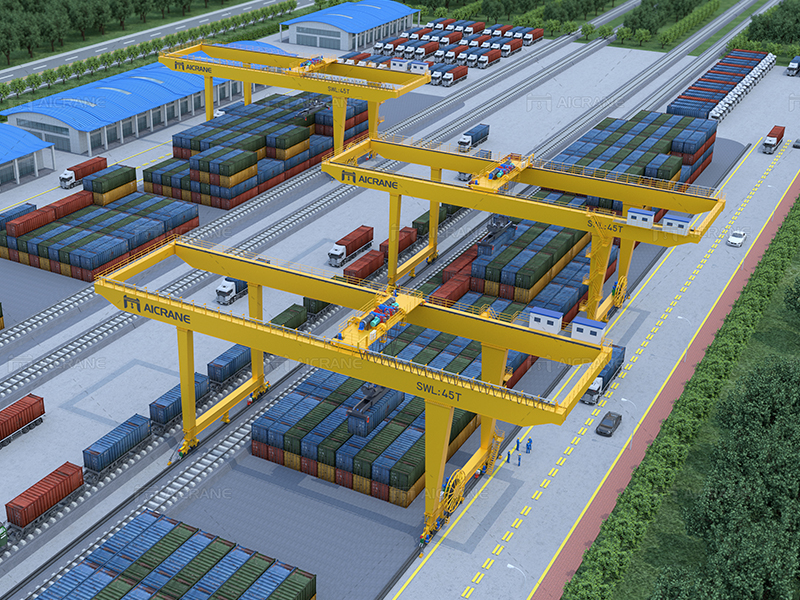
Overview of RMG Container Cranes:
RMG container cranes, as the name suggests, are gantry cranes that operate on rails. These cranes are designed to handle containers with remarkable accuracy, moving them between ships, trucks, and storage areas in bustling container terminals.
Key Components of RMG Cranes:
Rail-Mounted Structure: The defining feature of RMG container cranes is their rail-mounted structure. This design allows the crane to traverse along a set of rails, providing a stable and controlled path for the precise movement of containers.
Gantry Structure: The gantry structure consists of vertical and horizontal beams. The horizontal beam, known as the bridge, spans the width of the crane and supports the lifting mechanism.
Lifting Mechanism: The lifting mechanism comprises a spreader, hoist, and trolley. The spreader attaches to the container for lifting, while the hoist, powered by electric motors, raises and lowers the load. The trolley facilitates horizontal movement along the bridge.
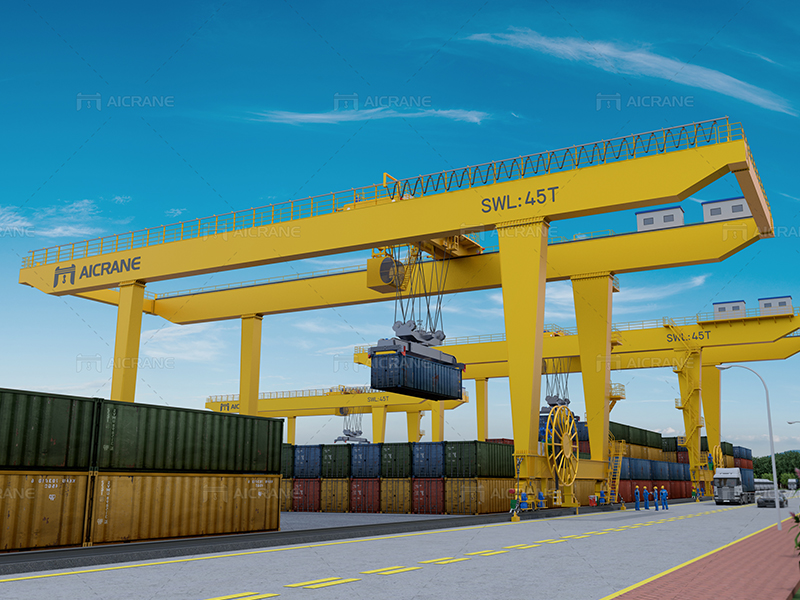

Working Principle of RMG Container Cranes:
Container Positioning: The RMG crane positions itself alongside the target container, ensuring precise alignment for the upcoming lifting operation. The rail-mounted structure ensures stability during this process.
Spreader Engagement: The spreader descends and securely engages with the container. The spreader’s twistlocks connect with the container’s corner castings, creating a secure attachment for the lifting process.
Lifting Operation: Electric motors power the hoist system, initiating the lifting operation. The container is smoothly raised off the ground, and the trolley allows horizontal movement along the bridge for accurate positioning.
Rail Traverse: Once the container is lifted and secured, the container gantry crane traverses along the rails to transport the container to its destination within the terminal. The rail-mounted design ensures stability and precise control during this movement.
Container Placement: Upon reaching the designated location, the hoist system gently lowers the container to the ground. The spreader disengages, releasing its grip, and the container is accurately placed in the desired spot.
Advantages of RMG Container Cranes:
Precision and Control: The rail-mounted design provides RMG cranes with unparalleled precision and control, ensuring accurate container handling within the terminal.
High Efficiency: RMG cranes are known for their efficiency in handling containers, contributing to the swift movement of goods in busy ports and terminals.
Optimized Use of Space: The rail-mounted structure allows for optimal use of space within the terminal, making RMG cranes suitable for locations with space constraints.
Conclusion:
Rail-Mounted Gantry (RMG) container cranes embody precision and efficiency in the world of maritime logistics. Their rail-mounted design and sophisticated lifting mechanisms make them indispensable for the smooth and controlled handling of containers within bustling terminals. As global trade continues to evolve, the role of RMG cranes remains pivotal in ensuring the seamless flow of goods across international ports. To learn more, visit https://steelmillcranes.com/
