Container gantry cranes play a crucial role in various logistics settings, including railways and container yards, facilitating efficient container handling operations. Understanding the main mechanism drive modes and layout forms specific to these applications is essential for optimizing performance and productivity. In this article, we will explore the different drive modes and layout forms commonly used in container gantry cranes for rail and yard operations. By examining their features and benefits, we aim to provide valuable insights into the design and operation of these vital machines.
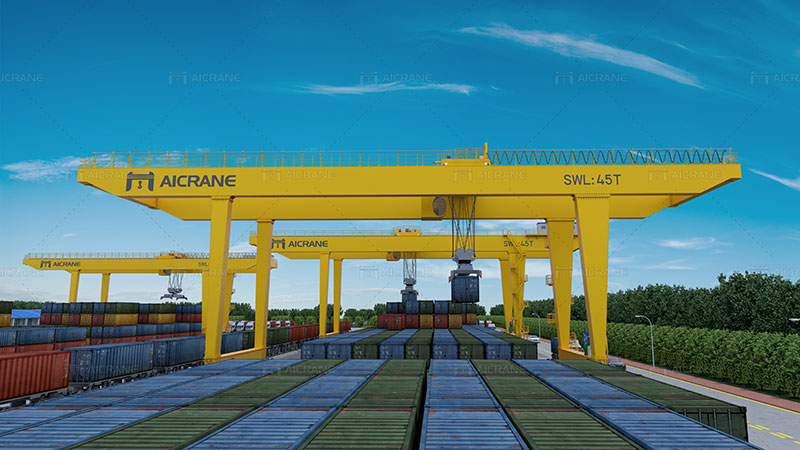

Main Mechanism Drive Modes of Container Gantry Cranes
Container gantry cranes used in railways and container yards often utilize specific drive modes tailored to their operational requirements. Here are three commonly used drive modes for these applications:
a) Electric Drive: Electrically driven container gantry cranes are widely employed in rail and yard operations. These cranes utilize electric motors to power their main mechanisms, such as hoisting, trolley travel, and gantry travel. Electric drive systems offer precise control, smooth operation, and low maintenance requirements. They are also energy-efficient, reducing operational costs and minimizing environmental impact.
b) Diesel Engine Drive: Some container gantry cranes in rail and yard settings are equipped with diesel engines as their primary drive source. This drive mode provides mobility and flexibility, allowing the rail mounted container gantry cranes to operate in remote locations or areas lacking a reliable electrical power supply. Diesel engine-driven cranes are suitable for applications where electrical infrastructure may be limited. However, they may produce higher noise levels and require regular maintenance and fuel replenishment.
c) Hybrid Drive: Hybrid drive systems combining electric and diesel engine technologies are increasingly being utilized in rail and yard applications. These systems offer the flexibility to switch between electric and diesel power sources, depending on operational requirements and power availability. Hybrid drive cranes provide the advantages of energy efficiency and reduced emissions, while also offering versatility in different scenarios.
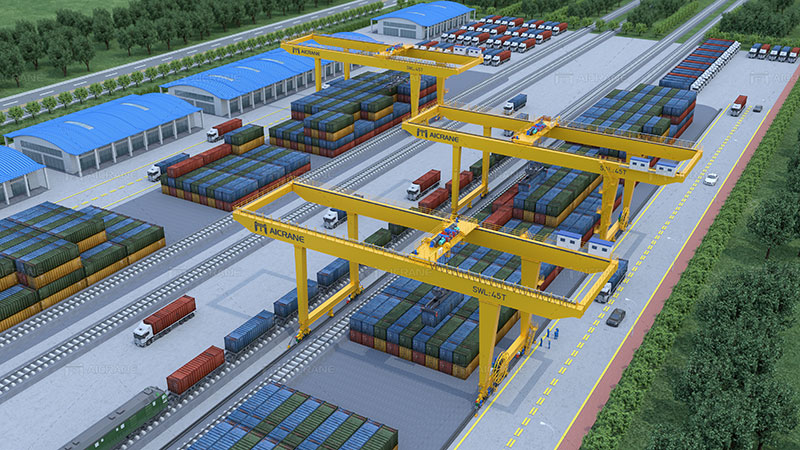
Layout Forms of Container Gantry Cranes
Container gantry cranes used in railways and container yards can adopt various layout forms based on specific operational needs. Here are three common layout forms for these applications:
a) Single Cantilever Gantry Crane: This layout form features a single cantilevered boom attached to the gantry structure. The trolley moves along the boom, allowing it to access containers within a specific span. Single cantilever gantry cranes provide a compact design, efficient operation, and easy access to containers along the rail tracks or in yard stacks.
b) Twin Cantilever Gantry Crane: Twin cantilever gantry cranes have two parallel booms mounted on the gantry structure. Each boom is equipped with a trolley that operates independently, enabling simultaneous handling of containers from adjacent rail tracks or yard stacks. This layout form improves operational efficiency by reducing the time required for loading and unloading multiple containers.
Each layout form offers specific advantages based on the operational requirements of railways and container yards. Factors such as container traffic, space availability, and efficiency considerations influence the selection of the most suitable layout form.
Conclusion
Container gantry cranes used in railways and container yards require specific drive modes and layout forms to optimize performance and meet the demands of these applications. Electric drive systems provide precise control and energy efficiency, while diesel engine-driven cranes offer flexibility in remote areas or locations with limited electrical infrastructure. Hybrid drive systems combine the benefits of both technologies. The choice of layout form, whether single cantilever, twin cantilever, or single leg, depends on container traffic, space constraints, and operational efficiency requirements. By selecting the appropriate drive mode and layout form, rail operators and container yard managers can enhance productivity, streamline container handling processes, and ensure smooth and efficient operations.
